Western culture is seen as the global standard. But is it normal human behavior?
The Ultimatum Game.
The rules are simple: in each game there are two players who remain anonymous to each other. The first player is given an amount of money, say $100, and told that he has to offer some of the cash, in an amount of his choosing, to the other subject. The second player can accept or refuse the split. But there’s a hitch: players know that if the recipient refuses the offer, both leave empty-handed. North Americans, who are the most common subjects for such experiments, usually offer a 50-50 split when on the giving end. When on the receiving end, they show an eagerness to punish the other player for uneven splits at their own expense. In short, Americans show the tendency to be equitable with strangers—and to punish those who are not.
[T]he game struck the Machiguenga as deeply odd: When he began to run the game it became immediately clear that Machiguengan behavior was dramatically different from that of the average North American. To begin with, the offers from the first player were much lower. In addition, when on the receiving end of the game, the Machiguenga rarely refused even the lowest possible amount. “It just seemed ridiculous to the Machiguenga that you would reject an offer of free money,” says Henrich. “They just didn’t understand why anyone would sacrifice money to punish someone who had the good luck of getting to play the other role in the game.”
With the help of a dozen other colleagues he led a study of 14 other small-scale societies, in locales from Tanzania to Indonesia. Differences abounded in the behavior of both players in the ultimatum game. In no society did he find people who were purely selfish (that is, who always offered the lowest amount, and never refused a split), but average offers from place to place varied widely and, in some societies—ones where gift-giving is heavily used to curry favor or gain allegiance—the first player would often make overly generous offers in excess of 60 percent, and the second player would often reject them, behaviors almost never observed among Americans.
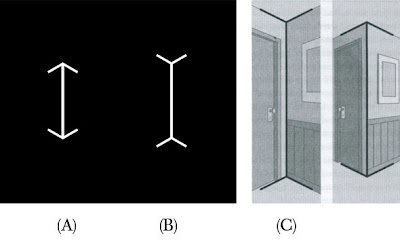
The Müller-Lyer illusion:
Researchers found that Americans perceive the line with the ends feathered outward (B) as being longer than the line with the arrow tips (A). San foragers of the Kalahari, on the other hand, were more likely to see the lines as they are: equal in length. Subjects from more than a dozen cultures were tested, and Americans were at the far end of the distribution—seeing the illusion more dramatically than all others.
Rod and Frame Task
Unlike the vast majority of the world, Westerners (and Americans in particular) tend to reason analytically as opposed to holistically. That is, the American mind strives to figure out the world by taking it apart and examining its pieces. Show a Japanese and an American the same cartoon of an aquarium, and the American will remember details mostly about the moving fish while the Japanese observer will likely later be able to describe the seaweed, the bubbles, and other objects in the background. Shown another way, in a different test analytic Americans will do better on something called the “rod and frame” task, where one has to judge whether a line is vertical even though the frame around it is skewed. Americans see the line as apart from the frame, just as they see themselves as apart from the group.
Social Pressure:
Asch had discovered that test subjects were often willing to make incorrect judgments on simple perception tests to conform with group pressure. When the test was performed across 17 societies, however, it turned out that group pressure had a range of influence. Americans were again at the far end of the scale, in this case showing the least tendency to conform to group belief.
What's fair?
As Heine, Norenzayan, and Henrich furthered their search, they began to find research suggesting wide cultural differences almost everywhere they looked: in spatial reasoning, the way we infer the motivations of others, categorization, moral reasoning, the boundaries between the self and others, and other arenas. These differences, they believed, were not genetic. The distinct ways Americans and Machiguengans played the ultimatum game, for instance, wasn’t because they had differently evolved brains. Rather, Americans, without fully realizing it, were manifesting a psychological tendency shared with people in other industrialized countries that had been refined and handed down through thousands of generations in ever more complex market economies. When people are constantly doing business with strangers, it helps when they have the desire to go out of their way (with a lawsuit, a call to the Better Business Bureau, or a bad Yelp review) when they feel cheated. Because Machiguengan culture had a different history, their gut feeling about what was fair was distinctly their own. In the small-scale societies with a strong culture of gift-giving, yet another conception of fairness prevailed. There, generous financial offers were turned down because people’s minds had been shaped by a cultural norm that taught them that the acceptance of generous gifts brought burdensome obligations. Our economies hadn’t been shaped by our sense of fairness; it was the other way around.
The Weirdest People in the World?
It is not just our Western habits and cultural preferences that are different from the rest of the world, it appears. The very way we think about ourselves and others—and even the way we perceive reality—makes us distinct from other humans on the planet, not to mention from the vast majority of our ancestors. Among Westerners, the data showed that Americans were often the most unusual, leading the researchers to conclude that “American participants are exceptional even within the unusual population of Westerners—outliers among outliers.”
Given the data, they concluded that social scientists could not possibly have picked a worse population from which to draw broad generalizations. Researchers had been doing the equivalent of studying penguins while believing that they were learning insights applicable to all birds.
Local culture is shorthand knowledge
He notes that the amount of knowledge in any culture is far greater than the capacity of individuals to learn or figure it all out on their own. He suggests that individuals tap that cultural storehouse of knowledge simply by mimicking (often unconsciously) the behavior and ways of thinking of those around them. We shape a tool in a certain manner, adhere to a food taboo, or think about fairness in a particular way, not because we individually have figured out that behavior’s adaptive value, but because we instinctively trust our culture to show us the way. When Henrich asked Fijian women why they avoided certain potentially toxic fish during pregnancy and breastfeeding, he found that many didn’t know or had fanciful reasons. Regardless of their personal understanding, by mimicking this culturally adaptive behavior they were protecting their offspring. The unique trick of human psychology, these researchers suggest, might be this: our big brains are evolved to let local culture lead us in life’s dance.